AI
AI and Machine Learning: Lighting the Way for Optical Advancements

Key Points
- AI and machine learning are increasingly driving innovation in the optical communication industry, especially in the short-reach optical transceiver market.
- These advancements in AI/ML will not only enhance data centers but also benefit broadband operators by supporting scalable, cost-effective solutions.
One of the key roles that CableLabs plays for our member operators and the vendor community is tracking trends in key areas of the broadband industry. Because the networks operated by our members are predominantly fiber, we are always keeping a close eye on the optical industry — but this year is proving to be an especially exciting one across a range of optical topics.
Short-Reach Optical Transceiver Market
What Optical Technologies Might Support AI/ML?
What Does This Mean for the Broadband Industry?
ECOC 2024
SCTE TechExpo24
Events
See You at OFC 2022

The 2022 Optical Fiber Communication Conference and Exhibition (OFC)—the hub of the optical industry and the premier event in fiber communications and networking—will take place March 6–10, 2022, at the San Diego Convention Center in San Diego, California. This year, the event will be presented in a hybrid format that offers both in-person and virtual sessions.
The Future of Cable
Wired
Everything You Want to Know About Coherent Optics for Access Networks (But Were Afraid to Ask)

The cable industry has been well served by its extensive fiber deployment that took place during the initial hybrid fiber-coax (HFC) buildout. Even though cable operators have answered capacity demand through fiber node-splits in specific high demand scenarios, only recently have operators embarked on deeper-fiber roll-out strategies as part of a comprehensive long-term evolution plan.
Wired
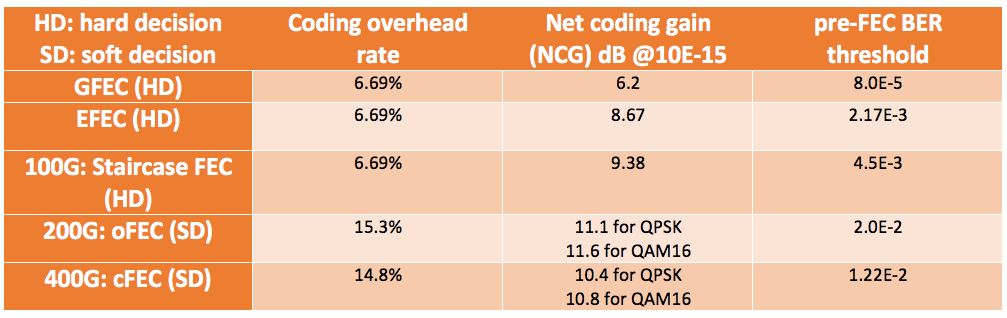
Forward Error Correction (FEC): A Primer on the Essential Element for Optical Transmission Interoperability

Forward error correction (FEC) has been a powerful tool in the cable industry for many years. In fact, perhaps the single biggest performance improvement in the DOCSIS 3.1 specifications was achieved by changing the FEC being used in previous versions – Reed-Soloman (RS) – to a new coding scheme with improved performance: low-density parity check (LDPC). Similarly, FEC has also become an indispensable element for high-speed optical transmission systems, especially in current coherent optical transmission age.
Wired
What is Full Duplex Coherent Optics?
A brand new innovation, Full Duplex Coherent Optics uses the same wavelength, in two different directions, over the same fiber at the same time. As a result, Full Duplex Coherent Optics technology supports over 200 times more capacity compared to non-coherent digital transmission over a single fiber. This makes Coherent Optics technology well suited for deployment in many more cable access network fibers. Watch our video to see how this technology will significantly increase the value of the currently deployed fiber infrastructure.
Wired
Doubling up on Fiber Capacity: A Winning Strategy for Full Duplex Coherent Optics

During our 2017 Winter Conference, CableLabs announced the launch of the point-to-point (P2P) Coherent Optics specification project, potentially multiplying the capacity of each existing cable access network fiber by over 100 times and possibly indefinitely deferring new fiber builds on existing routes. Now, a new CableLabs innovation, Full Duplex Coherent Optics:
Why CableLabs Began the Coherent Optics Project
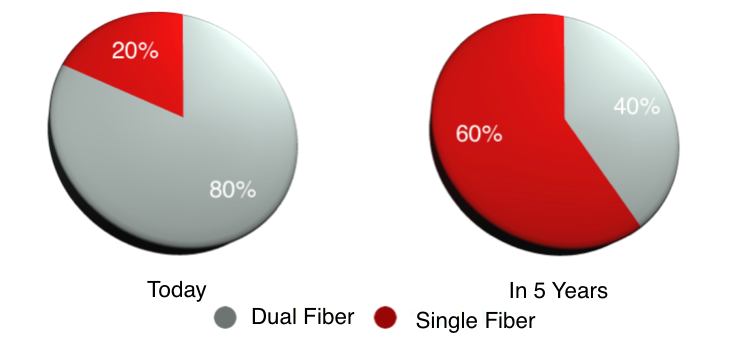
Transport Methodologies
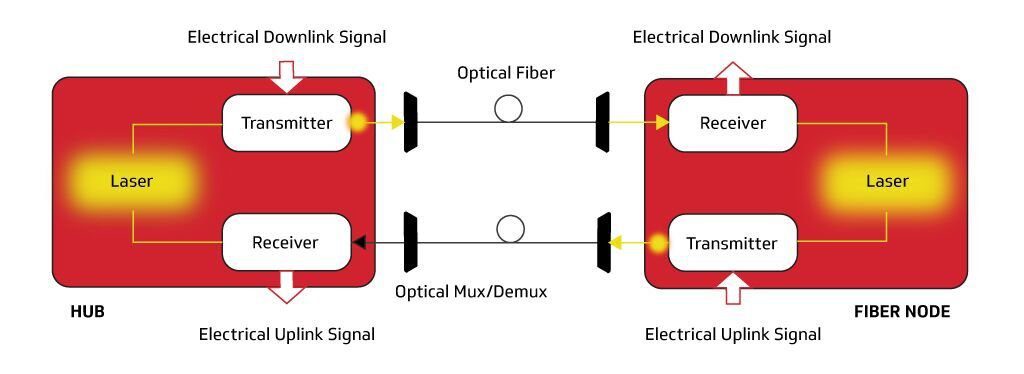
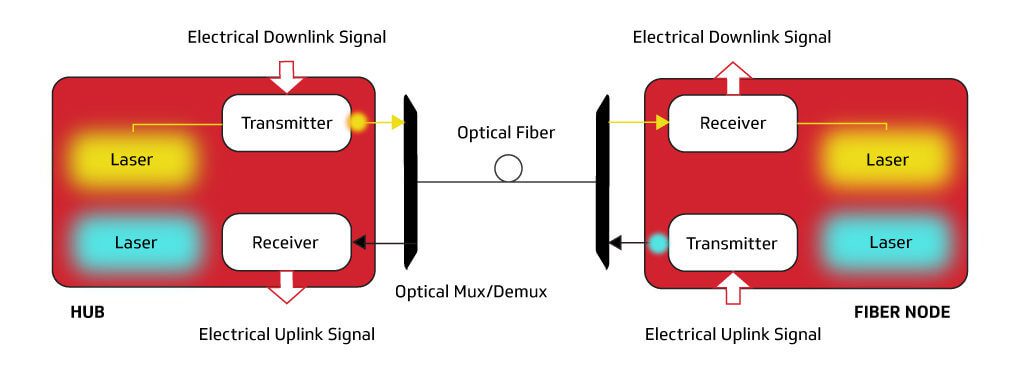
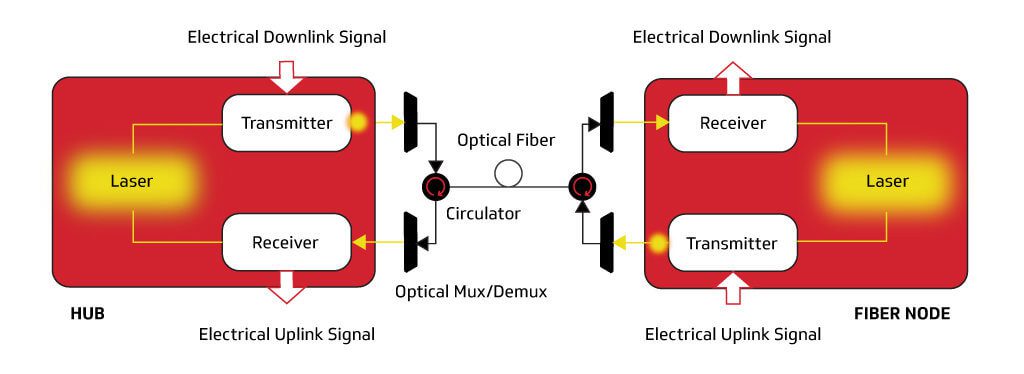
The Dual-Fiber Approach
The Single-Fiber Approach
CableLabs’ Full Duplex Coherent Optics Approach
How Does It Work in a Cable?
Impacts/Benefits of Full Duplex Coherent Optics
Wired
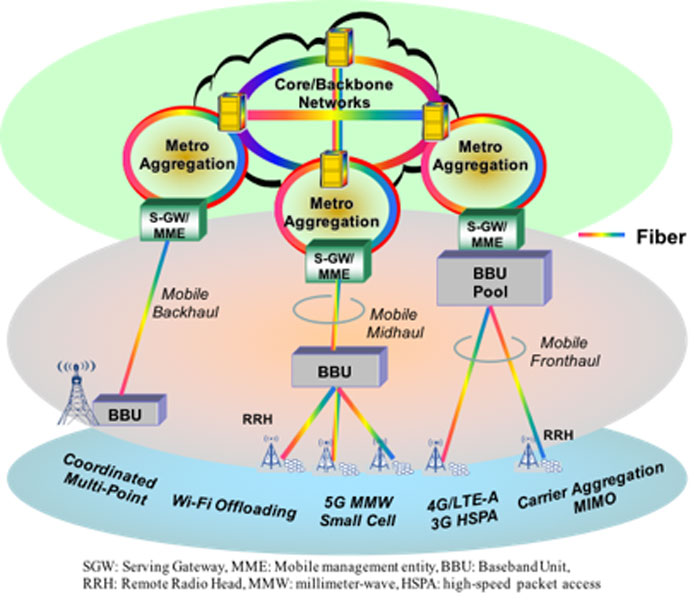
It’s Only Wireless for THIS long

Why the underlying fiber network is critical to mobile communications. -- The explosion in popularity of the mobile game Pokémon Go has triggered unprecedented attention on virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). Many believe that Pokémon Go is just the first step into the fully-immersive VR and AR applications, which, from a bandwidth demand perspective, are on the high end of the Internet of Things (IoT) connections. By the end of this decade, analysts predict that 50 billion IoT sensors will connect to mobile networks consuming 1000 times as much data as today’s mobile gadgets alone. Along with cloud, machine to machine, and new video streaming applications, the underlying network infrastructure that enables such constant high-quality connectivity is critical to ultimate user experiences. None of the existing radio access technologies will be able to individually provide the capabilities to effectively meet market demands. The next generation 5G mobile system is being designed specifically to support this vision of satisfying the increasing demand for higher data rates, lower network latencies, better energy efficiency, and reliable ubiquitous connectivity.