Innovation
CableLabs Open Source LPWAN Server Brings Diverse LPWAN Technologies Together

CableLabs is excited to announce a new open source project called LPWAN Server. The LPWAN Server provides new capabilities to bring IoT LPWAN wireless technologies together.
Before we go into more details on the LPWAN Server, let us first get some background into this space. In my previous blog post, I discussed the Internet of Things (IoT) as a growing industry comprised of a massive number of devices that connect to each other to benefit our lives. For example, a soil moisture sensor can help a farmer determine when to water their crops rather than potentially wasting water through a legacy timed-based approach. In that blog post, CableLabs announced the release of an open source LoRaWAN solution, LoRa Server.
What is LoRa Server and LPWANs?
LoRa Server is a community-sourced open source LoRaWAN network server for setting up and managing LoRaWAN networks. LPWANs connect sensors designed to last for years on a single battery transmitting information periodically over long distances.
There are many potential use cases shown below:
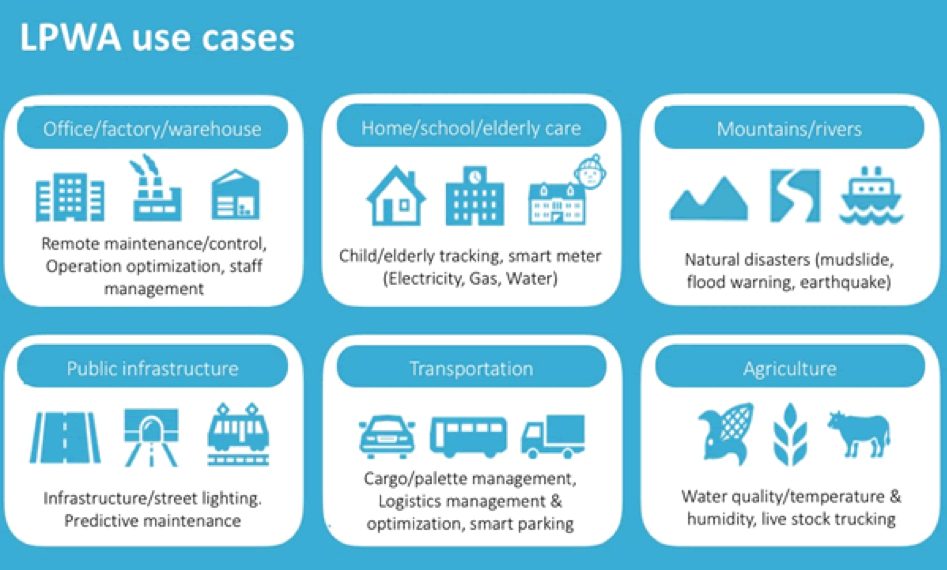
LPWA use cases graphic by LoRa Alliance member Actility at the occasion of its collaboration with Softbank in Japan.
LPWANs are designed to cover large geographical areas and minimize the amount of power required for sensors to interact with the network. There are many solutions available to enable these use cases, including:
- LoRaWAN™: LoRaWAN is a partially open unlicensed spectrum solution developed through the specifications efforts of the LoRa Alliance: While the specifications are developed within the Alliance, they are made available to the general public upon completion.
- Mobile solutions from 3GPP: 3GPP defined Cat-M1 and NB-IoT for varying connectivity requirements. These are also open standards, but they require licensed spectrum.
- Weightless: Weightless is an open specification effort but has struggled in gaining traction in the LPWAN space. It should be noted, there are many other proprietary LPWAN technologies with active deployments and use in this ecosystem.
Why No One Solution Will Own the Technology
We believe no one LPWAN technology will fully own this IoT space. Our reasoning for this belief comes from multiple factors. As we look at the sensors in this space, some are intended for real-time applications with consistent and verified uploads, while other sensors simply wake-up periodically and transmit small data payloads. Without going into more specific examples, we believe some LPWAN applications are better suited for licensed spectrum mobile networks, while other LPWAN applications are better supported with unlicensed solutions, such as LoRaWAN™. LoRaWAN services can be further explored through some of our member offerings via MachineQ™ and Cox℠ .
Our New Open Source Solution
With these considerations in mind, we developed a new open source solution to enable easily moving data from devices and applications across varying network types and related solutions. The LPWAN Server was designed to enable multiple use cases:
- First, it can be used to simply migrate or operate between two LoRaWAN™ network servers, such as the LoRa Server and The Things Network.
- Second, and more importantly, the long-term design intention is to enable the routing of multiple LPWAN technologies, such as LoRaWAN™ and SigFox or LoRaWAN™ and Narrow Band IoT (NB-IoT). In order to integrate IP-based devices, the server will include a “relay server” of sorts. This allows for the IP traffic to mix with LoRaWAN™ traffic for a single upstream interface to an application or data collector, such as Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure.
Our goal with this project is to see developers add more back-end integration with network servers and technologies to enable this routing of traffic across many LPWAN technologies.
LPWAN Server Use Cases
The LPWAN Server was designed to support the following use cases:
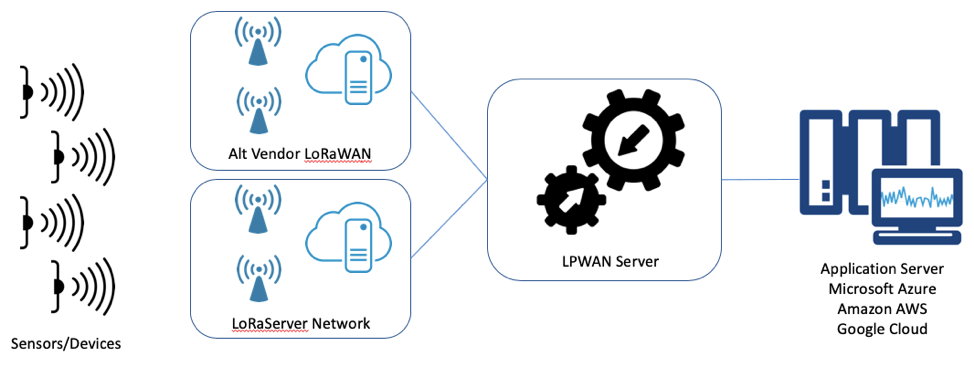
1. Multi-vendor LoRaWAN™ environment: Using the LPWAN Server in a multi-vendor LoRaWAN™ environment allows a network provider to:
- Test multiple servers from multiple vendors in a lab,
- Trial with multiple network servers from multiple vendors
- Run multiple vendor solutions in production
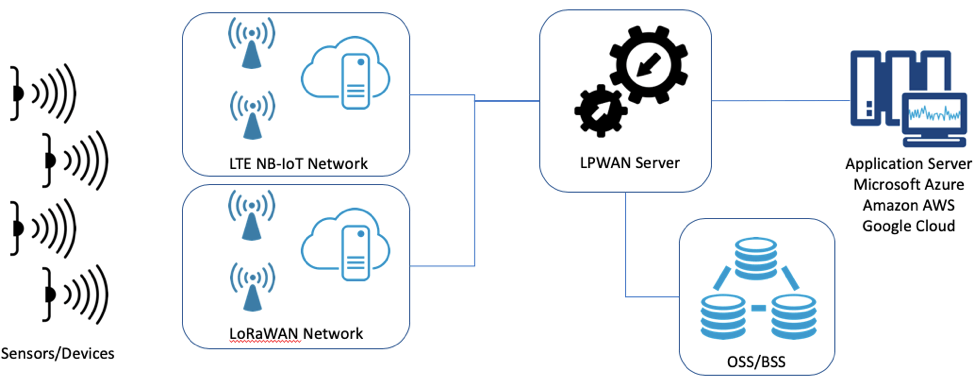
2. NB-IoT & LoRaWAN™ device deployment: The LPWAN Server will allow you to operate a single application for devices deployed on both LoRaWAN™ and NB-IoT networks. The LPWAN Server will enable an IP relay-server for connecting with NB-IoT (and Cat-M1) devices commonly behind a 3GPP mobile network Evolved Packet Core (EPC). It also allows for managing devices on the LoRaWAN™ The devices are managed under a single application within the LPWAN Server. This allows an application to receive data over a single northbound Application Program Interface (API) rather than maintain API connections and data flows to multiple networks.
3. Simplify device provisioning across multiple LPWAN network types and solutions: The LPWAN Server simplifies provisioning to one or more LPWAN networks. A major challenge for a back-office solution is to integrate provisioning into a new network server. This is further complicated with multiple new network servers and types. In order to simplify this, the LPWAN Server manages the APIs to the networks, and the back-office solution only needs to integrate with a single API to the LPWAN Server. The following figure illustrates this.

4. Create consistent data order and formats from LPWAN devices: The final use case explains how the LPWAN Server can normalize data from varying devices on one or more networks. Unfortunately, even in a single network environment, such as LoRaWAN™, there is no standard for data formats from multiple “like” sensors. For example, a weather sensor from two different vendors could send the same type of data but reverse the order. An application will need to interpret the data format from multiple sensors. In order to simplify this, the LPWAN Server can be used to reformat the data payload into a common format for sending up to the application server. In this way, the application server will not need to interpret the data.
CableLabs & the Development Community Together
The LPWAN Server is intended to be a community open source project. The initial release from CableLabs provides support for a multi-vendor LoRaWAN™ use case. The back-end has been designed for future support of all of the use cases, and the UI is flexible to support them as well. We currently are using the server for data normalization, too; however, this is via a back-end process.
The open source community is encouraged to take advantage of the initial CableLabs development and further the development into a useful application for even more servers, solutions and use cases. There are many network types and related servers, and we would like the development community to help us integrate these.
To find out more information about the LPWAN Server and become involved in this project, go to https://lpwanserver.com.
The LPWAN Server was designed to work with the CableLabs sponsored open source LoRa Server. In an upcoming blog, I will discuss how that project continues to evolve and align with the latest specification releases from the LoRa Alliance. The LPWAN Server and LoRa Server provide a comprehensive solution to enable many LPWAN use cases.


