Wireless
MWC 2024 Buzz Signals Continuing Momentum for 5G and Other Mobile Technologies
Key Points
- Hot topics at MWC 2024 in Barcelona included 5G, Network as a Service (NaaS), AI, Open RAN and more.
- Although there were fewer announcements about disruptive, new 5G technologies than in recent years, activity during MWC suggested overall forward movement is continuing in the development of 5G solutions.
Mobile World Congress (MWC) is the flagship conference for the mobile industry, where vendors and mobile operators showcase new products, technologies and solutions. The buzz at the annual trade show translates to the pulse of the mobile industry and offers a sneak peek at its direction.
This year at MWC Barcelona, more than 100,000 participants attended from 200-plus countries, and more than 2,700 small and large vendors and operators were on exhibit across eight halls. The level of activity at the event was on par with pre-pandemic levels.
Here are a few general observations and themes from this year’s MWC.
‘Show Me the Money’
Every year, there is huge anticipation for announcements about disruptive technologies or new solutions in the mobile industry. This year, the impact of new developments and disruptive 5G solutions was muted compared with years past — somewhat expected, as operators are still undergoing 4G-to-5G network transitions, awaiting releases to complete their fully featured 5G networks.
Operators who haven’t yet seen the expected monetization from their 5G build-outs are cautious about upcoming investments toward continuing the rollout of the network. Overall, a limited number of solutions showcased at the show could be categorized as “money-making” for operators.
However, the news wasn’t all negative! Vendors and operators demonstrating Network as a Service (NaaS) solutions were pretty common. CableLabs even presented a demonstration illustrating potential applications of NaaS on the fixed network.
In addition, the event partner co-located with the MWC — “4 Years From Now” (4YFN) — had its largest-ever showing, with start-up and venture-capital companies coming together to showcase the state of what’s possible with 5G networks. This was a very popular part of the show.
AI Will Enhance Efficiencies in 5G
Artificial intelligence (AI) was a common theme among 5G vendors and operators demonstrating efficiencies in 5G service delivery, throughput, operations and performance. However, nothing was truly disruptive.
The AI solutions were focused on operator-specific network improvements to squeeze out 5G network performance, using AI to improve their return on investment (ROI) in place of spending on additional 5G network rollout.
In addition, AI was generally tailored to vendor-operator partnerships for specific 5G network improvements and use cases using prototype solutions still under development. Overall, the role of AI in 5G networks was a hot topic, but there were no clear answers to questions about how the technology might ultimately impact the industry.
Network Virtualization and Disaggregation Continues to Advance
Network operators and vendors continue to disaggregate network components and virtualize network functions as shown by many advanced solutions on exhibit for the 5G core and RAN. This includes both operator-based on-premises virtualization along with cloud-based services from third-party service providers. This shows the continuing network evolution toward virtualization, providing new services, reducing costs and enhancing operational efficiencies.
6G Still in Early Stages
There was little 6G activity. Most of the 6G activity was centered around test equipment to help enable and develop ideas and proof of concepts. With 5G still being deployed and a few years from its full features, it seems that 6G is in the early stages of ideation in the academic, vendor development and standards community.
Open RAN Continues to Gain Momentum
Open RAN vendors showcased further evolution of disaggregated and virtualized RAN solutions, featuring more capabilities and more availability of common uses that include macro cells, small cells, fixed-wireless access (FWA) and private networks. Improved functionality included higher-level MIMO RU solutions such as 32×32 and 64×64 MIMO in the mid-band.
There was also advancement in RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) and Service Management and Orchestration (SMO) platforms, with various Open RAN partnerships showcasing capabilities closer to commercial operation. Again, in many cases, these advances were specific to operator and vendor partnerships, so Open RAN via the O-RAN Alliance has a ways to go before realizing its final vision.
Other Hot Topics
Other topics discussed at the show included the following:
- The Internet of Things (IOT) remains a potential key trend for 5G networks. Vendors and operators alike showcased many use cases and product solutions.
- The use of non-terrestrial networks (NTNs) for mobile communications is starting to make progress. Advances in satellite technology are making the technology a viable option for traditional voice communications in unserved rural areas and as a backup alternative during network outages.
- Energy efficiency and sustainability continue to be top of mind for operators. Most vendors are providing solutions to help drive down energy consumption and improve long-term sustainability.
All in all, the buzz at MWC was relatively quiet with no major announcements or industry disruptions related to these and other mobile technologies. However, considering the large attendance, the conference was filled with lots of activity and steady forward movement in 5G development. This could bode well for the industry as it continues with its 5G rollout.

Wireless
Enriched Wi-Fi Performance Through Wi-Fi Multimedia

Key Points
- A collaboration between CableLabs and Meta found that Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) could improve the performance of voice/video calling applications when it is enabled on an access point.
- Given the positive results from the testing, operators might consider using WMM to ensure the necessary throughput, low latency and managed jitter for time-sensitive applications such as these.
- The details of the testing and results are included in a technical report available for download below.
Network service providers and application developers both work to provide their users with the best possible quality of experience (QoE) for their respective services. Although many segments of the service/application layer of end-to-end networks are out of the operator’s control, the segments between the user’s device and the internet are not.
One such critical and consistent segment within the home network is Wi-Fi — the preferred and most commonly used network access technology in the home. This last link has become synonymous with the overall internet. Ensuring the best throughput and latency of these services/applications will reflect on the user’s experience and therefore determine how good or bad the internet service is.
Not all applications have similar traffic needs with regard to throughput, latency and jitter. One such category of applications is Real Time Communication (RTC), examples of which include voice/video calling applications such as Messenger and online meeting applications such as Zoom and Microsoft Teams. To ensure necessary throughput, low latency and managed jitter for RTCs, providers might consider the use of the Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) feature.
Wi-Fi Multimedia in Test Scenarios
WMM has four categories of traffic: Voice (VO), Video (VI), Best Effort (BE) and Background (BG). Traffic within each of the categories is given different priorities. Without WMM enabled, all traffic is treated equally, meaning that web browsing and email exchange, for example, are treated the same as time-sensitive applications such as RTCs.
A collaboration between CableLabs and Meta examined the WMM feature to determine the potential for overall improvements to an RTC application. The results of this testing showed that — with WMM enabled on the access point (AP) — RTC applications had improved quality of video and audio, even with varying traffic-load conditions on the Wi-Fi network. In addition to weathering changing traffic loads, RTC quality was maintained as the RTC device moved over varying distances from the AP.
Testing involved emulating a single-family dwelling using three locations. At each location, the RTC client was placed close to the AP (near), midway from the AP (mid) and at the AP’s serving edge (far). Test scenarios consisted of two types of contention traffic: The first introduced typical traffic as seen in a home setting, representing the use of various home applications, and the second fully loaded the Wi-Fi network with simulated traffic. Throughout the testing, the RTC device was shifted to different static distances from the AP (near, mid, far) and QoE was measured in every case. Testing also included a sweeping test case in which the RTC client was moved from near, mid and far locations (in relation to the AP) and then returned to the near location simulating a person moving within the home (sweep). Tests were conducted in the 2.4 GHz band using a 20 MHz channel, as well as the 5 GHz band using an 80 MHz channel.
The results showed that, with WMM enabled, RTC applications experienced improved performance compared with RTC applications not using WMM. This outcome was consistent over all testing: static at near, mid and far locations, and while moving the device from near to edge and back.
Reporting on WMM Testing Results
The details of the testing and results are available in a technical report, “Impacts of WMM on Wi-Fi — Study of Real-Time Communication Quality and WMM.” CableLabs is eager to take these positive lab results and test them in the field to prove the benefits of WMM in real-world environments. After downloading and reviewing the test reports and results, members are encouraged to contact me if they are interested in participating in trials to prove the benefits in a real-world environment.

Technology Vision
Connectivity Without Limits: CableLabs Unveils Transformative Technology Vision

Key Points
- CableLabs’ Technology Vision is a strategic roadmap to support the broadband industry through innovation and technology development over the next decade.
- It is designed to foster a healthy, competitive ecosystem, enabling seamless connectivity services that provide differentiation for CableLabs’ member operators.
- The Tech Vision also will drive industry alignment and unmatched scale for our members and the vendor community.
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, connectivity is more essential than it ever has been before. It’s as much a part of our lives as the air we breathe. It’s all around us — the lifeblood of nearly every facet of our digital lives. And it puts the broadband industry at the forefront of some of the most promising innovations that will guide us into a future of ever-expanding potential.
That’s why we’re excited to unveil a fresh strategy for CableLabs and the work we do on behalf of the industry: the CableLabs Technology Vision.
Bolstered by three future-focused pillars, this Tech Vision serves as a roadmap for advancing innovation and technology development over the next decade. It aims to foster alignment and create unmatched scale for the industry — building a healthier, more competitive ecosystem for CableLabs’ member operators and the vendor community.
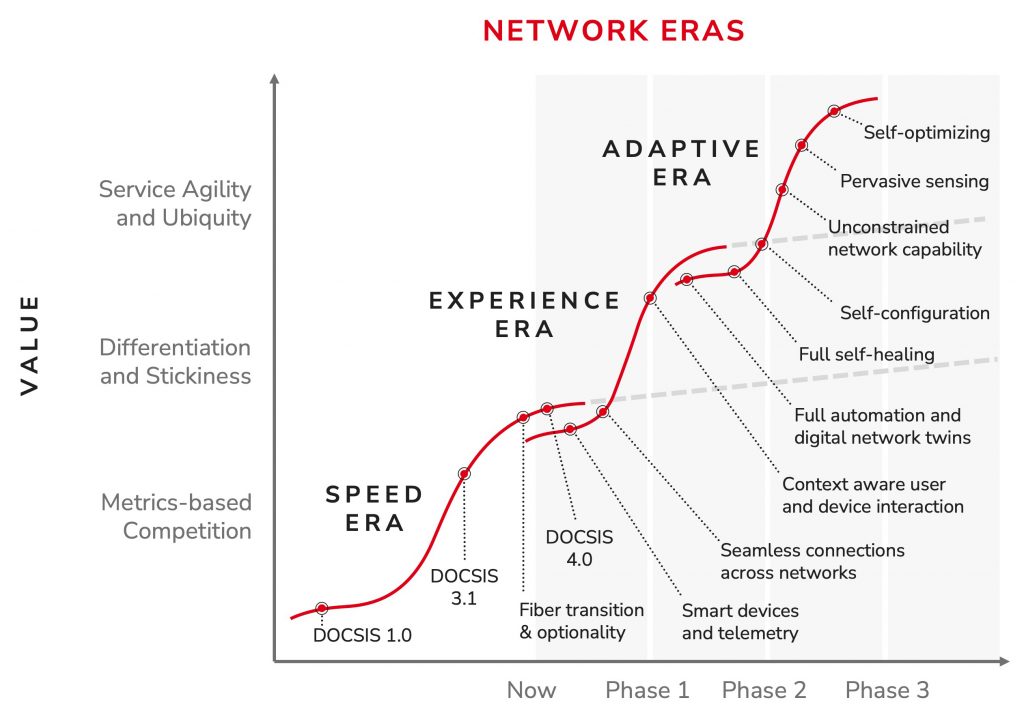
CableLabs’ Tech Vision supports a new era of connectivity, propelling the evolution of the network from one primarily focused on speed to one that adapts to the needs of users and devices in real time. By setting a target for ubiquitous, context-aware connectivity and an adaptive, intelligent network, this vision will create new opportunities for better, more seamless online experiences.
Key Themes of the CableLabs Technology Vision
In our Tech Vision, CableLabs prioritizes a trio of key themes that encompass the scope of this technology innovation. Together, these areas offer a concise model for discussing how our technology innovations relate in our work within the industry to build an adaptive network.
Seamless Connectivity
Seamless Connectivity is the first of these key themes. It’s connectivity wherever a user is, on whatever device they’re using, on whichever network they happen to be tapping into — all without them needing to give it a second thought. It enables connectivity without concern for the access network or how a user is moving across the network. Because it’s context-aware, the network stands ready to adapt services to match the needs of the user’s interactions, operating quietly behind the scenes to ensure a consistently smooth and secure online experience. Seamless Connectivity enables:
- Enhanced user experiences that make connectivity possible anywhere, on any device
- Unparalleled in-home experiences
- Context-aware user and device interactions
- Fixed-mobile convergence such as capabilities for seamless subscriber session and traffic steering
Network Platform Evolution
The path toward a secure, seamless user experience lies in evolving our network platforms. It’s this critical aspect of our Tech Vision — the key theme of Network Platform Evolution — that will pave the way for innovations that create the most efficient network architectures. These architectures will offer unprecedented optionality and unmatched flexibility for CableLabs’ member operators, allowing them to deliver the truly seamless connectivity experiences their customers demand. At a glance, Network Platform Evolution offers opportunities for:
- Network scalability and ecosystem development
- End-to-end automation
- Access network evolution and convergence
- Fiber transition and optionality
- Next-generation network capabilities based on AI and new computing architectures
Pervasive Intelligence, Security & Privacy
Secure and trustworthy foundations are paramount in today’s connected world. That’s where our final theme — Pervasive Intelligence, Security & Privacy — comes in. Simply put, it’s intelligence at every point in the network. It ensures high performance, reliability, security and privacy for all users and devices in any connectivity context, allowing users to connect with confidence and peace of mind in any environment. This theme enables:
- Smart, dynamic networks that leverage APIs, telemetry and AI technologies
- Post-quantum security, user-centric privacy and zero trust
- Capabilities to make networks more energy-efficient and sustainable, pointing to sustainability as a first principle
- Integration of intelligent devices and automation, telemetry and monitoring platforms throughout the network to achieve higher levels of reliability and performance
Collaboration, Collaboration, Collaboration
Collaboration has been a cornerstone of CableLabs’ mission since our start in 1988. Together with our members, the vendor community and other industry stakeholders, we have fueled innovations in connectivity. By renewing our focus with this new Tech Vision, CableLabs aims to create transparency and hone our focus to more efficiently support these partners. We'll continue to help define standards and specifications to ensure greater compatibility, interoperability and progress for all of us in the ecosystem.
We work closely with our member teams, vendor companies and other standards bodies to ensure maximum scale and interoperability for the broadband industry. Some of those key industry organizations include ITU-T, IEEE, IETF, WBA, WFA, BBF, TIP, GSMA, CAMARA, 3GPP and others. We are always looking to engage on behalf of our members to foster industry collaboration.
Advancing the Industry, Advancing Society
The CableLabs Technology Vision is a roadmap for the future of connectivity, setting a course for a more intuitive, efficient and secure online experience for everyone. It will shape the network to adapt to user needs and unlock new possibilities for operators and their customers.
But it’s more than a framework. It’s our future.
Through this work, CableLabs is driving innovation and empowering our members to take part in a vibrant, collaborative ecosystem. Our work will pave the way to a more connected, intelligent and secure tomorrow. As demand grows for more robust digital experiences, this vision lays the foundation for a future where our networks are more adaptive, intelligent and secure — a tomorrow where connectivity is ubiquitous.
We welcome our member and vendor community to join us in realizing this potential for our industry. Connect with us using the button below to collaborate with us on this journey.
By embracing this vision and working together, we can unlock a world of possibilities. Our Tech Vision will allow operators and their customers — as well as society as a whole — to navigate the ever-evolving digital landscape with confidence and ease. Together, we’re shaping the future, one connection at a time.

Fiber
Common Provisioning and Management of PON: A New Working Group Launches

Key Points
- In keeping with CableLabs’ focus on optical fiber solutions, we have announced two new working groups to support the cable industry’s deployment of optical technologies.
- The near-term focus for this effort will be for ITU PON and 25GS-PON, however the work will be applicable to other next-gen PON flavors.
- Vendor neutrality through device interoperability is a key objective of the activity.
Consistent with the strategy outlined in a recent blog, CableLabs has recently launched two new working groups related to fiber to the premises (FTTP). Information on one of the working groups — Optical Operations and Maintenance — can be found here. The subject is this blog is the provisioning and management of passive optical networking (PON) in cable access networks.
As the cable industry has begun to deploy multiple gigabit service, there’s a growing current of enthusiasm and interest for the efficient deployment, management and maintenance of those access networks. Furthermore, the speed at which technology is moving is impressive and expensive. It can be difficult for cable operators to keep pace with these advancements, which require a matrix of expertise and decision-making.
PON is one of the technologies that keeps marching forward. CableLabs has been developing PON-based specifications for over a decade, and we’re continuing in that vein to help operators lower barriers for deploying and operating fiber networks.
Common Provisioning and Management of PON
Common Provisioning and Management of PON is another working group that CableLabs recently launched. This group will focus on provisioning and management solutions for PON technologies. With the support of operators and vendor partners, CableLabs previously developed specifications to support DOCSIS Provisioning of EPON (DPoE). The new working group will be laser-focused on 10G Symmetrical PON (XGS-PON), with applicability to 25GS-PON and higher-speed next-generation ITU PON technologies.
To develop a common provisioning framework, this group will be tackling several assignments that will support the provisioning and adjacent solutions needed for various deployment requirements. All this work will be folded into the target objectives. These will include (but are not limited to) complete provisioning of XGS-PON, common service and device configurations, and vendor neutrality.
What the Work Entails
So, how will we accomplish these objectives? Through various operator presentations and vendor proposals, we’ve determined that our near-term work plans will include the following:
- Identifying operator use cases.
- Analyzing existing cable modem configuration files to support a DOCSIS translation layer.
- Building an ONU Management Control Interface (OMCI) cable profile to support the use cases.
Operator use cases. Operator use cases will include residential and commercial service offerings — for example, identifying triple-play services (e.g., HSD, voice, video), backhaul and other necessary services. This identification will be the easy part, considering the fact that we must include many of the service offerings that operators deploy today.
DOCSIS translation layer. You’re probably asking yourself, “Why is DOCSIS in this list of activities?” Some cable operators would like to leverage their existing DOCSIS back office to support the provisioning of non-DOCSIS technologies. Think DPoE, which CableLabs released in 2011. For those operators that want to leverage their DOCSIS back-office investment, DOCSIS configuration files will be analyzed to better understand those use cases. The configuration will include Type Length Value (TLV) parameters and Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Management Information Base (MIB) objects to satisfy the use cases. This configuration can then be translated to OMCI Managed Elements (MEs) to configure and manage the ONU.
OMCI cable profile. PON technologies based on the International Telecommunication Union’s Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) use OMCI to configure and manage an ONU. Although the G.988 standard contains a large set of managed entities (MEs), this working group will determine what’s necessary for cable ONU configuration and management. As such, this effort will build an OMCI “cable profile” that will support a common set of managed elements. These MEs may be grouped together or adjusted to include the appropriate configuration required for the various identified use cases. The OMCI cable profile would be a superset of all MEs across the list of uses cases but a subset of the entire G.988 Recommendation. The OMCI cable profile can be used to support both the DOCSIS and non-DOCSIS back-office infrastructure, and in this respect improve the interoperability of OLTs and ONU in any case.
Interoperable Solutions
In its entirety, this work will create a complete process to provision and manage XGS-PON (and future ITU PON flavors) in a cable access network. It will allow vendors to incorporate interoperable solutions in their product portfolios that operators can then leverage with their service offerings.

Policy
The Case for Additional Unlicensed Spectrum

Key Points
- Wi-Fi provides internet connectivity for the vast majority of devices and applications, in terms of both the number of connections and total data carried.
- To keep pace with performance increases of internet services and with the growing performance demands of critical devices and applications, U.S. and global governments must continue to allocate additional unlicensed spectrum toward the advancement of Wi-Fi performance.
Today and for the foreseeable future, Wi-Fi is the technology most devices and applications use to connect to the internet. As technology advances, those devices and applications will require more data to deliver high-quality experiences for increasingly immersive, compute-intensive applications. To further support the emergence of high-fidelity video conferencing, cloud gaming, virtual reality (VR)/augmented reality (AR) and other immersive applications, widespread availability of 10 gigabit and 25 gigabit internet services is just over the horizon.
The real-time nature of these cutting-edge applications will require even faster and higher-performing Wi-Fi, with greater throughput, lower latency and better reliability. Also, because consumers primarily rely on Wi-Fi to connect to the internet — demonstrated by 10 times the amount of data going over Wi-Fi compared with mobile networks and the roughly 80 percent of data from mobile devices going over Wi-Fi — consumers now expect wall-to-wall Wi-Fi coverage in their homes, businesses and wherever they are (e.g., airports, coffee shops, civic centers). More unlicensed spectrum is key to ensuring that Wi-Fi performance keeps pace with consumer expectations and needs.
Identifying and allocating additional unlicensed spectrum for Wi-Fi is critical to ensuring the ready distribution of increasingly capable internet services throughout the home and enterprise. Such efforts will enable the increased performance of today’s and tomorrow’s critical applications in terms of coverage, throughput, latency and reliability, and will support new Wi-Fi features and functionality. In opening the 6 GHz band to Wi-Fi and other unlicensed use in 2020, the FCC took a necessary step toward enhancing the performance and capabilities of Wi-Fi and ensuring the future growth of broadband. However, opening 6 GHz isn’t a one-and-done solution. Additional unlicensed spectrum is needed to enable continued Wi-Fi performance enhancements to stay ahead of both the increasing performance of broadband networks and the growing performance requirements of devices and applications.
Background
Since its inception, Wi-Fi has been designed to use spectrum efficiently and to co-exist with other spectrum users. Wi-Fi uses a contention-based protocol and seeks to transmit data opportunistically in short bursts, when the frequency channel is available, enabling coexistence with other users. Moreover, Wi-Fi devices use a half-duplex access protocol (transmitting and receiving on the same channel) to further economize on available frequency channels.
In 1997, IEEE released the first 802.11 standard, which is the basis for Wi-Fi. From that humble beginning, we’ve seen the adoption of Wi-Fi explode. Today, there are more than 21 billion Wi-Fi devices in use globally. Initially, Wi-Fi used the 2.4 GHz band and provided a data rate of up to 2 Mbps. Over time, Wi-Fi devices began using the 5 GHz band and larger channel sizes to drive increased data rates. With Wi-Fi 6E and the incorporation of channel sizes up to 160 MHz, Wi-Fi devices can support data rates over 1 Gbps.
With the opening of the 6 GHz band (5.925–7.125 GHz), the FCC enabled for the first time 320-MHz Wi-Fi channels. Doing so required the FCC to craft an innovative three-part sharing framework to enable coexistence with the incumbent licensees:
- Low Power Indoor (LPI) requires the use of a contention-based protocol, permits only indoor access points (APs), restricts those APs to a power spectral density limit of 5 dBm/MHz and total power limit of 30 dBm EIRP on a 320-MHz channel, and is available across the entire 6 GHz band.
- Standard Power, enabled by Automated Frequency Coordination (AFC), allows outdoor access points and higher power, up to 36 dBm EIRP (or 23 dBm/MHz on 20 MHz channel), when under the control of an AFC system, and is only available in the UNII-5 (5.925–6.425 GHz) and UNII-7 (6.525–6.875 GHz) portions of the band.
- Very Low Power (VLP) requires the use of a contention-based protocol and enables indoor and outdoor operations at an even lower power limit of -5 dBm/MHz and is only available in the UNII-5 and UNII-7 portions of the band.
The Wi-Fi Alliance officially released Wi-Fi 7 on January 8, 2024. With the available 320 MHz channels in 6 GHz, Wi-Fi can now deliver speeds over 10 Gbps (using four MIMO streams), helping to ensure that Wi-Fi keeps pace with advances in internet service speeds and increasing application requirements.
Driving the Need for Additional Unlicensed Spectrum
U.S. and other governments must continue to allocate additional spectrum for unlicensed use not only to keep pace with the growing demand for Wi-Fi and other unlicensed technologies but also to remain ahead of the technology curve. Allocating additional unlicensed spectrum will fully enable and maximize the benefits of emerging applications and functionality, which will translate to an expected $5 trillion in annual global economic value by 2025. The drivers of necessary additional unlicensed spectrum are discussed below.
Increasingly capable broadband services and growing consumer demand for more connected devices, higher throughput, lower latency and increased reliability. History has made clear that total data usage and bandwidth requirements will only grow in coming years and most of that data will be carried over Wi-Fi, as noted above. This growth will be enabled by the ubiquitous availability of increasingly capable broadband services: 10 gigabit and beyond (e.g., DOCSIS 4.0, 10G-EPON, XGS-PON, 25G-PON). To this end, the U.S. government is investing well over $40 billion to deploy highly capable fiber-based networks. Data and bandwidth usage growth will also be driven by more connected devices and increased use of real-time and data-intensive applications such as new interactive VR/AR experiences. We’ve seen the average number of connected devices per home grow from 13 in 2021 to 17 in Q3 2023 — an increase of over 30 percent in less than two years and a trend we expect to continue. We also continue to see average fixed broadband residential data usage increase — currently, on average, over 640 GB per month. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption and use of video conferencing and other cloud-based tools. As the FCC has explained, “video conferencing has grown from a niche product to a central pillar of our communications infrastructure.” Because consumers no longer connect devices using an ethernet cable, but rather rely on Wi-Fi to connect to the internet, the government must also continue to make additional unlicensed spectrum available to ensure the government’s investment in broadband deployment actually reaches end-devices and enables the critical applications of today and tomorrow.
Supporting new features and functionality of Wi-Fi 7 and beyond. Additional unlicensed spectrum is also needed to make room for the coming features and functionality of Wi-Fi 7 and beyond. The release of Wi-Fi 7 introduced new features and functionality; of note, Wi-Fi 7 now includes support for 320 MHz channels and Multi-Link Operation (MLO). Both features enable higher throughput and lower latency through the use of wider channels and multiple channels — features not available in prior generations of Wi-Fi. Moreover, IEEE is already working on 802.11bn, the standard that will underpin Wi-Fi 8. The emerging focus is on Ultra High Reliability (UHR) where additional spectrum becomes even more critical to meet performance goals in light of potential channel contention from high-density client environments, adjacent Wi-Fi networks or other unlicensed use.
The technical limitations enabling the 6 GHz innovative sharing framework. The FCC’s innovative unlicensed sharing framework in 6 GHz is a huge success, protecting mission-critical incumbents and allowing for expanded Wi-Fi use at the same time. Moreover, this sharing framework eliminated the need to relocate incumbents, enabling the rapid realization of the benefits of this additional unlicensed spectrum to consumers and enterprise users alike.
To ensure safe coexistence, the FCC established a detailed unlicensed spectrum sharing framework, including Low Power Indoor-only (LPI) restrictions across the band and more recently Very Low Power (VLP) restrictions and database-controlled (by an AFC database) standard-power capabilities available in certain parts of the band, as detailed above. To accommodate these restrictions, Wi-Fi requires more bandwidth to deliver high speeds and employs more spectrum-intensive techniques, such as mesh networking, to achieve the needed coverage. For example, mesh networking requires additional overhead to backhaul and coordinate the mesh traffic, reducing the overall data-carrying capacity of the available channels. One approach to avoid mesh networking is to use a higher-power channel. However, under the current FCC rules, Wi-Fi can access, at most, only one standard-power 320 MHz wide channel through an AFC system.
Between the power limits and other regulatory restrictions placed on LPI and VLP operations and the limited availability of standard power channels under an AFC, the 1,200 MHz available for unlicensed use in the 6 GHz band is unable to provide the needed coverage, throughput, capacity and latency performance that will be expected and required by consumers and enterprise users in the near future. Additional unlicensed spectrum will allow consumers and enterprise users to more fully benefit from Wi-Fi 7’s new features, enabling better user experiences.
It’s Up to Government
Taking all these drivers into account and considering the value that unlicensed spectrum will continue to deliver to global economies, the United States and other governments around the world should waste no time identifying meaningful additional unlicensed spectrum, particularly given that any additional unlicensed spectrum will likely have similar regulatory technical limits as 6 GHz unlicensed use.

Events
CableLabs Winter Conference: Powering Connections and Collaboration This Month in Orlando

Key Points
- Winter Conference is designed for CableLabs members and the NDA vendor community to expand their knowledge, build meaningful connections and discover the technology advancements transforming the industry.
- Sessions will cover topics including AI, Wi-Fi, seamless connectivity, optics and DOCSIS® technology — as well as an all-new Technology Vision for the industry.
Are you ready to maximize your connections and unlock opportunities for collaboration? Join us at CableLabs Winter Conference — an exclusive event bringing together industry experts and thought leaders to foster progressive dialogue and help shape the future of broadband.
This private, intimate gathering is a unique opportunity for our members and the NDA vendor community to expand knowledge, network with peers and discover the technology advancements transforming the industry.
CableLabs’ much anticipated and most requested event is back in Orlando, Florida, from March 25–28, 2024. Registration is open for members through March 20, and on-site registration will be available at the conference.
Voices of the Industry
Craig Moffett, industry analyst and Senior Managing Director of MoffettNathanson, will set the scene with his perspective on the current state of the industry as well as emerging trends and opportunities.
Later, industry executives Ron McKenzie of Rogers Communications, Elad Nafshi of Comcast Cable and Gary Koerper of Charter Communications will discuss the industry’s new and evolving Technology Vision in a strategic, forward-thinking session led by CableLabs’ SVP and CTO, Mark Bridges. This new vision will foster more robust, efficient and sustainable industry ecosystems.
Among the other featured Winter Conference speakers are Victor Esposito, CTO at Ritter Communications, who will discuss FTTH and PON strategies, and Dan Rice, Vice President of Access Network Engineering at Comcast Communications. He will participate in a panel exploring the most pressing topics around network platform evolution.
A Spotlight on Strategy
A series of all-new strategy sessions are planned for members to exchange ideas and practical insights on Thursday, March 28. A Broadband Usage and Demand Forecasting session, which will include breakfast that morning, will kick off the day — covering the evolution of network demand and its impact on future technology and capacity planning.
The breakfast will be followed by deep-dive sessions on seamless connectivity strategies using mmWave spectrum and Low-Earth-Orbit Satellite technologies, and the market dynamics and economics of FWA and FTTH. Members must be registered for Winter Conference to attend these strategy sessions.
Captivating Content
Winter Conference is packed with insights and inspiration. Just some of the additional conference session topics include:
AI and Autonomous Networks
- Learn about the transformative effects of ongoing AI endeavors and discuss how the industry can unite to create a more interconnected and intelligent network ecosystem.
FTTH and PON
- Discuss challenges to FTTH deployment, accelerating network deployment, and the modernization and virtualization of PON.
- Explore the future of PON — including emerging technologies such as 25G, 50G and 100G PON, quality-based access networks, seamless connectivity and reliability.
Seamless Connectivity
- Get a Wall Street expert’s view on how telcos are positioning themselves for seamless convergence.
- Explore the growth drivers and early use cases of Global Developer Services.
Wi-Fi
- Hear about the challenges of supporting the in-home Wi-Fi experience and strategies needed for quick and effective resolution of issues.
- Explore the strategic role of Wi-Fi in ensuring a high-quality, seamless in-home broadband experience, and gain insights into the latest developments.
And that’s not all! There’s so much more to discover and learn at Winter Conference.
Smaller Market Conference
At the Smaller Market Conference on Monday, March 25, small and mid-tier operators will have the opportunity to discuss the issues that are most important to them and their teams. This event is available for CableLabs members and NCTA guests. Registration for Smaller Market Conference is separate from Winter Conference, so please be sure to register for both if you are planning to attend.
Experience Winter Conference
Don’t miss the chance to take part in one of the highlights of the CableLabs events calendar. Expand your knowledge, build meaningful connections and stay at the forefront of industry advancements.
Visit the event website to register and plan your trip to CableLabs Winter Conference today.

Fiber
Future-Proofing Optical Networks: Streamlining Operations for a Smooth Transition to PON
Key Points
- Cable operators desire to simplify operations while they embrace passive optical networking (PON), but maintaining and managing PON solutions is proprietary, different from other access networks and requires new tooling.
- Some unification of fault and failure management is desirable for the industry so that operators can reduce the need to swivel chair between networks and tools, and vendors can simplify what they support in their products.
- PON, like other optical networks, relies on proprietary management tools based on, at times, telemetry that is proprietary or extended from any of a number of standards or specifications.
- From our experience with DOCSIS technology, by helping the industry align on operations, CableLabs knows this could all be better for everyone.
Imagine you’re a network engineer trying to manage the capacity of your DOCSIS networks — and suddenly you’re tasked with learning a whole new set of additional tools, techniques and terminologies to manage a new type of access network: a passive optical network (PON).
Now apply that complexity to the entire operations, the many involved technicians and all the necessary tools to accomplish the task. That’s the level of difficulty that many network operators face today as they begin to deploy PON technology for their access networks. Maintaining and managing PON solutions is largely proprietary — and very different from other access networks, requiring new tooling and expertise.
Needless to say, operators are in the midst of a massive transition. Instead of operating a few flavors of DOCSIS® networks, they’re managing an even broader set of technologies in their access networks. But these challenges don’t need to be as significant as they are.
By aligning the industry with certain architectures and identifying the key telemetry, building solutions that support use cases in ways that streamline operations, and reducing the burden of broad and overlapping options for vendors, we can shrink the time to market for improved technologies while streamlining our networks overall.
To help operators rise to the challenge, CableLabs is not only committing resources in this direction but has also established a working group called Optical Operations and Maintenance (OOM) that tackles the aforementioned complexities head-on.
The Optical Operations and Maintenance Working Group
The OOM working group has the scope of aligning fault and failure management of optical networks to streamline operations. The stated objectives of this program and working group are to “reduce troubleshooting and problem resolution time and costs while increasing network capacity and uptime.” These objectives include:
- maintenance that is proactive, reactive, predictive and more
- attention to the physical layer and related functions
- telemetry alignment, solution development and more
If you've been around the industry a bit, these objectives might seem familiar. Indeed, the OOM working group’s objective statement is very similar to that of CableLabs’ Proactive Network Maintenance (PNM) working group. We could have called OOM “Optical PNM,” but we recognize that operators have goals beyond PNM when it comes to optical networks. Our charter for this work matches what operators and vendors say they need.
Although that scope seems large (and it is!), OOM is also focused on quickly turning around valuable results. The current course of the working group is like a peloton of bicycles in a race: In a cooperative effort, OOM will share outcomes with a parallel working group that addresses other fiber to the premises (FTTP) challenges since the working group is indeed addressing one FTTP challenge—common provisioning and management.
By working together, we accelerate the work of both groups. When it comes time for OOM to move to the next optical challenge, we'll have the momentum we need to push forward.
Creating Industry Alignment Through Standards and Specifications
Architecture is the foundation for operations in that network operations must manage the network components and systems. How the network does its job to provide service — and how it fails to do so — drives what needs to be managed and monitored. Fault and failure monitoring use cases drive the information needed, and therefore the network telemetry and other data that network operators need.
The architecture connects through the system failures and service impacts to the telemetry that supports the network operations use cases. Through a traceability approach, OOM identifies the necessary telemetry that addresses operator needs, choosing from existing standards and specifications when possible. The process we follow will create industry alignment on what is important in standards and specifications today. That methodology eases the burden for vendors.
Reducing complexity is a first alignment step, but we also want to drive consistency. That consistency will focus on current cable operations as well as the other networks they manage. By targeting PON options that align best with DOCSIS network advantages that operators enjoy today, we reduce the operations burden. It then becomes possible to agree on common tools, and thereby reduce the cost of network operations. By enabling the alignment of optical network management, we take that one step further.
We’ve already seen the potential of OOM's work in PON, but the next steps will present a whole new challenge. Introducing aligned use cases to connect the architecture to the telemetry can reduce the complexity of vendor developments and operator tools. We have to drive that advantage to other networks, too.
Looking Ahead to New Optical Challenges
Those next optical challenges I mentioned before? We’ll set our sights toward the core next: other forms of optical access, optical trunk systems such as point-to-point (P2P) coherent optics, Metro Optical Ethernet (MOE) and backhaul and ring and mesh systems, regional optical networks, backbone networks, and maybe beyond. One could say there is light at the end of the fiber!
If you see this as an opportunity to streamline your business in the optical world, engage with CableLabs on any of a number of our optical networking efforts and consider being a part of the OOM working group. We invite you to see the light!

DOCSIS
Combined DOCSIS 4.0 Interop Event Stresses Network Interoperability and Virtualization
Key Points
- The recent Interop•Labs event combined systems and components to demonstrate multi-supplier interoperability across the DOCSIS 4.0 ecosystem.
- Test scenarios included combining DOCSIS 3.1 and DOCSIS 4.0 equipment to demonstrate additional flexibility for operators.
- Interoperability is key to creating a healthier ecosystem because it enables more competition and operator scalability.
CableLabs and Kyrio hosted a combined DOCSIS® 4.0 technology and Distributed Access Architecture (DAA) Interop•Labs event February 12–15 at our headquarters in Louisville, Colorado. This was the first combined interop between CableLabs and its subsidiary, and the involved suppliers and operators made it a success.
At this Interop•Labs event, the exercises included both DOCSIS 4.0 cable modems and Remote PHY equipment, including virtualized cores and Remote PHY Devices (RPDs) that support DOCSIS 4.0 technology. During the week, mixing and matching of systems and components demonstrated multi-supplier interoperability across the DOCSIS 4.0 ecosystem.
Interop Takeaways
Casa Systems, CommScope and Harmonic brought DOCSIS 4.0 cores to the interop, and Casa Systems, Cisco, CommScope, DCT-DELTA, Harmonic, Teleste and Vecima brought RPDs that offered a mix of DOCSIS 3.1 and DOCSIS 4.0 technologies. Arcadyan, MaxLinear and Ubee Interactive showcased DOCSIS 4.0 modems. Rohde & Schwarz also participated with its DOCSIS 4.0 test and measurement system. Operators attended to observe the interop, interact with the suppliers and talk about their DOCSIS 4.0 technology plans.
The focus of the interop was interoperability across the ecosystem. A common test scenario at the event involved a virtual core from supplier A, an RPD from supplier B and a DOCSIS 4.0 modem from supplier C, all connected and operating according to specifications. The products were mixed and matched to investigate interoperability scenarios, with suppliers pitching in to analyze the results. To demonstrate extra flexibility for cable operators, suppliers mixed DOCSIS 3.1 and DOCSIS 4.0 equipment because the specifications are written for cross-compatibility.
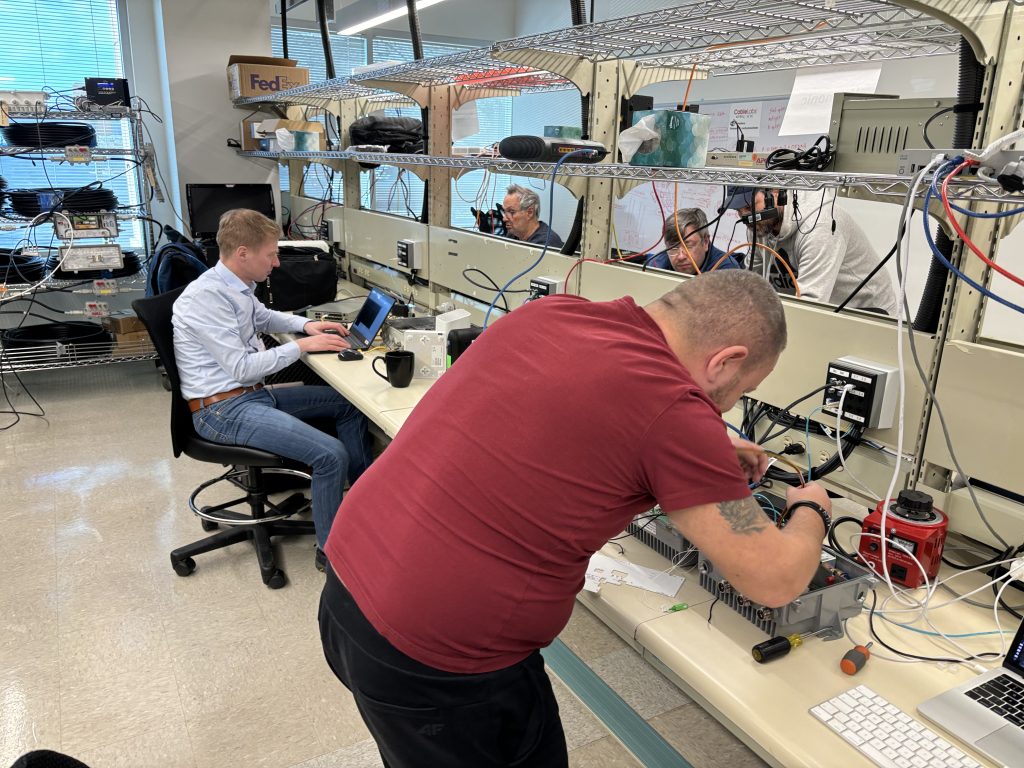

Above, engineers collaborate during the first combined DOCSIS 4.0 Interop•Labs event hosted by CableLabs and its subsidiary, Kyrio.
Interestingly, the interop illustrated how the traditional cable modem termination system (CMTS) has been disrupted by virtualization. Provided by one supplier, the CMTS used to be one box that did it all. Now, the software components have been abstracted into a virtual core that runs on servers in our data center, while the physical-layer components have migrated to the fiber node. This virtual architecture provides both better scalability and improved flexibility for the software, as well as better physical-layer performance on the coaxial cable. And in between, the fiber-optic cable uses much more scalable digital Ethernet connections.
The interop also demonstrated that the core and fiber node components can come from different suppliers because that interface is described in the CableLabs Remote PHY specifications. Looking at interoperability from all angles benefits all stakeholders. Interoperability enables a larger market in which suppliers can compete, which leads to varying competitive strategies and healthier ecosystems. Interoperability gives operators the confidence to plan large installations and the certainty that the equipment they put in the field this year will work for years to come.
Remote PHY interoperability events began in 2017 with DOCSIS 3.1 technology, so these solutions have been in the field for years and have matured. This interop shows that the migration to DOCSIS 4.0 technology is both very far along and proceeding smoothly — and that the supplier community has embraced interoperability among system components.
It's About Network Cohesion
The integration and optimization of the DOCSIS 4.0 ecosystem is underway. The goal has moved beyond simply booting DOCSIS 4.0 modems. Rather, we’re putting together all the parts, mixing and matching from different suppliers, demonstrating interoperability across the interfaces defined in CableLabs specification and achieving the multi-gigabit speeds and other advanced capabilities of DOCSIS 4.0 technology such as security, low latency and proactive network maintenance.
Other parts of the DOCSIS 4.0 ecosystem are also becoming available, including hybrid fiber coax (HFC) network equipment such as amplifiers, taps and passives.
To learn more about this exciting evolution, join us next month at CableLabs Winter Conference. This exclusive event for CableLabs members and the NDA vendor community will explore DOCSIS technology in two powerful sessions: “Unleashing the Full Potential of the DOCSIS 4.0 Network” and “A Vendor Perspective on DOCSIS 4.0 Technology Implementation.” You’ll hear from industry leaders about effective strategies, opportunities and benefits of the DOCSIS 4.0 network. Join us!

Convergence
Embracing the Future with Network as a Service (NaaS)

Key Points
- NaaS enables developers to write applications that work across networks and network operators using a single, simple API.
- It streamlines communication and coordination between applications and the underlying network — improving network efficiency and reducing service complexity.
- This approach is more flexible, scalable and user-centric than other current solutions.
In our increasingly connected world, the demand for seamless, fast and efficient online experiences is growing at an unprecedented rate. Imagine a network where your services follow you, enabling an experience that is unique to you — wherever you are, on any device.
This is where Network as a Service (NaaS) steps in, promising to revolutionize the way we interact with the digital world. Let's dive into the what, why and how of NaaS.
Optimizing Online Experiences
In today’s home network, we are simultaneously connecting more devices and running more applications than ever before — all creating the countless online experiences we encounter every day.
What if we could manage these new experiences more efficiently, ensuring that the network is adapting to our needs? That’s precisely the goal NaaS aims to achieve.
By leveraging context awareness, NaaS enables a network that is more responsive to those different devices and applications while giving users a new level of control over their services.
The Impact of Enhancing Connectivity
Improving the underlying network infrastructure isn’t just about eliminating minor inconveniences. It's about unlocking a world of possibilities.
For users, that means an enhanced online experience with faster, more reliable access to services. For operators, it opens up new avenues for revenue through the delivery of new, more advanced network services. Most significantly, it enables a robust, agile network as the foundation for future technologies and experiences in the home and on the go.
NaaS stands at the forefront of this transformation, ensuring that as our digital demands evolve, our networks aren’t just keeping up but leading the way.
What Is Network as a Service?
NaaS is a new approach to networking. It acts as a bridge between the applications we use and the underlying network, allowing for an unprecedented level of communication and coordination.
In simple terms, NaaS lets applications request the network services they need when they need them, thereby ensuring an optimal experience through dynamic network controls. NaaS enables developers to write applications that work across networks and across operators — all through a single, simple API.
This evolved architecture improves the network's efficiency and reduces the complexity of deploying and managing services. Compared with existing solutions, NaaS provides a more flexible, scalable and user-centric approach, heralding a new age of digital connectivity.
A collaboration between CableLabs and Liberty Global, Explorer WiFi leverages NaaS to provide a private network and enhanced Wi-Fi services for guests of hotels and short-term rentals. Video Provided by Liberty Global
The Future of NaaS and CableLabs' Role
The NaaS journey is just beginning. As we look toward the future, we see a digital landscape where networks aren’t just infrastructure but intelligent platforms that adapt to our needs in real time.
CableLabs is committed to leading this transformation, working closely with our members and the vendor community to explore, develop and deploy NaaS solutions. Through working groups, webinars and collaborative projects, we plan to take advantage of the ample opportunities for involvement and stay at the forefront of this network innovation.
Your Invitation to Shape the Future of Networking
Are you excited about the possibilities NaaS offers? Do you want to be part of this digital revolution?
Whether you're a developer, an operator or simply someone passionate about the future of technology, your insights and contributions are valuable. To learn more and find out how you can get involved, click the button below. Together, we can build a more connected, efficient and innovative digital world.
If you’re attending MWC Barcelona 2024, come see NaaS in action. Alongside Liberty Global and Vodafone Ziggo, CableLabs will present a demo illustrating potential applications of NaaS on the fixed network. Look for us in the GSMA booth located in Hall 4, Stand 4F30.
The future of networking isn’t only about faster speeds and more connections; it's about creating a smarter, more responsive infrastructure that anticipates and adapts to our needs. That’s what NaaS is all about.
Join us on this exciting journey!

AI
Intelligence (It’s Artificial): Takeaways From the CES 2024 Show Floor

Key Points
- In his CES 2024 report and an accompanying CableLabs webinar, broadband industry professional Clarke Stevens explores the role of AI in new innovations.
- AI-powered technologies rely on strong network connectivity — opening up a world of opportunity for broadband operators.
If you attended CES in Las Vegas, you’re probably finally starting to emerge from your technology-overload coma and trying to make sense of it all. We’ve got you covered!
If you haven’t read it yet, check out my recap from the annual trade show: “Clarke’s CES 2024 Report: Are You Smarter Than Your Technology?” I hope it will get you thinking about some of the great technologies that were on display and even entertain you a bit.
In the event, however, that you’re prioritizing your real job over reading my (admittedly lengthy) report, we’ve still got you covered! CableLabs is sponsoring a webinar in which I’ll discuss the technologies and solutions I saw and give my analysis on how they’re relevant (or not) to the broadband industry and to consumers in general. If you’re a CableLabs member, register now for the webinar on March 6.
In the meantime, here’s a brief summary to whet your appetite.
AI Spreading Outward
The primary theme of the show was that intelligence is becoming artificial. You might believe you already know all about artificial intelligence (AI), but now the technology is becoming more pervasive, spreading to common electronics.
Consider, for example, the Flappie cat door, whose motion sensor and night-vision camera will keep an eye on your cat and prevent him from coming inside the house until he drops the mouse he’s captured. Other AI-powered tools enable you to also measure your vitals just by looking in a mirror or communicate with people in your own voice when you can’t speak like you used to.
Because products like these rely on strong network connectivity, broadband operators will be an innate part of their success with customers. The industry opportunity doesn’t end there. Somebody must install, provision and maintain these products. Operators have the technical staff, vehicle fleets and monthly billing relationship with customers that give us a distinct advantage in the pursuit of new business opportunities beyond simple connectivity.
AI also presents operators with the prospect of new, futuristic market opportunities. AI-assisted cameras in cities can identify vehicles, animals and people. They can spot vehicle congestion and reroute traffic, and even call police, ambulances or firefighters.
AI Focused Inward
Cable companies can also use AI to anticipate, repair and even proactively prevent problems in their own network infrastructure. The benefits include a more reliable network at a reduced cost, fascinating new revenue opportunities and an improved ability to meet high-demand needs and provide appropriate service levels. Our combination of proven networking technologies and private networks can be leveraged to provide continuous connectivity to support new business models or simply make existing businesses more efficient.
A sometimes-overlooked opportunity in our industry is to increase our customer base by engineering our solutions toward new kinds of customers. For example, AI-powered “glasses” for the blind can replicate some of the benefits of a guide dog (sadly, not love). Not only can they guide a person around obstacles, but they can also integrate GPS for navigation and even help identify items on a grocery shelf. Let’s see the dog do that!
Many companies today are focused on conducting their business with an eye toward sustainability. Electric vehicles of every kind are replacing fossil-fueled alternatives. Fancy “leather” goods are being manufactured from pineapple waste. Bioengineered house plants are being bred to work as efficient (and decorative) air filters.
And, as always, great people are a natural advantage for the cable industry. AI and the other emerging technologies featured at CES are allowing those people to be more efficient, productive and happy.
A Limitless Future
New technology is improving your health, your daily life and your bottom line. You owe it to yourself to learn more about the emerging AI technologies that will make a difference in your near future.
In the webinar on March 6, I’ll cover some of the crazy ideas that blossom on the way to innovation. This is the kind of conversation that will improve your water cooler game as you stand around your Nube “no-plumbing” water generator that condenses and purifies moisture from thin air!